Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
topology/3dBorderExtraction.cpp
Objects have a border, which are the points which touch the complement in the sense of background adjacency. A border of an object is itself an object, with the same topology as the object.
- See also
- Border of a digital object
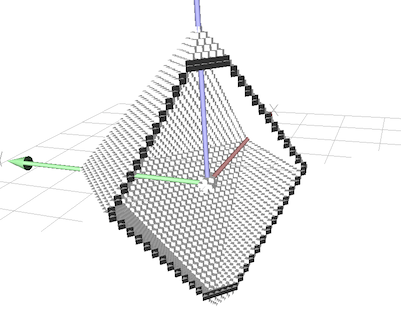
Border extraction visualisation
#include <iostream>
#include "DGtal/base/Common.h"
#include "DGtal/io/readers/VolReader.h"
#include "DGtal/io/viewers/PolyscopeViewer.h"
#include "DGtal/io/Color.h"
#include "DGtal/images/ImageSelector.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/StdDefs.h"
#include "ConfigExamples.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DGtal;
{
typedef MetricAdjacency< Z3, 2 > Adj18;
Adj6 adj6;
Adj18 adj18;
DT6_18 dt6_18( adj6, adj18, JORDAN_DT );
typedef Domain::ConstIterator DomainConstIterator;
Point p1( -50, -50, -50 );
Point p2( 50, 50, 50 );
Point c( 0, 0 );
// diamond of radius 30
DigitalSet diamond_set( domain );
{
if ( (*it - c ).norm1() <= 30 ) diamond_set.insertNew( *it );
}
ObjectType diamond( dt6_18, diamond_set );
// The following line takes almost no time.
ObjectType diamond_clone( diamond );
// Since one of the objects is modified, the set is duplicated at the following line
diamond_clone.pointSet().erase( c );
ObjectType bdiamond = diamond.border(); // one component
ObjectType bdiamond_clone = diamond_clone.border(); // two components
MyViewer viewer;
viewer<< Color(250, 250,250);
viewer << bdiamond_clone;
viewer << bdiamond ;
viewer << ClippingPlane(1,1,0,5);
viewer.show();
return 0;
}
// //
Aim: A wrapper class around a STL associative container for storing sets of digital points within som...
Definition DigitalSetByAssociativeContainer.h:90
Aim: Represents a digital topology as a couple of adjacency relations.
Definition DigitalTopology.h:96
Aim: Parallelepidec region of a digital space, model of a 'CDomain'.
Definition HyperRectDomain.h:100
Aim: Describes digital adjacencies in digital spaces that are defined with the 1-norm and the infinit...
Definition MetricAdjacency.h:80
Aim: An object (or digital object) represents a set in some digital space associated with a digital t...
Definition Object.h:120
Definition PolyscopeViewer.h:56
Definition SpaceND.h:96
Definition testClone2.cpp:346
DGtal is the top-level namespace which contains all DGtal functions and types.
Definition ClosedIntegerHalfPlane.h:49
STL namespace.