Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
geometry/meshes/digpoly-curvature-measures-cnc-3d.cpp
Computation of mean and Gaussian curvatures on a mesh defined by a an implicit shape discretized as a digital surface, using constant or interpolated corrected curvature measures (based on the theory of corrected normal currents). It uses a digital normal vector estimator to improve curvature estimations. Errors with respect to true expected curvatures are also computed.
This first example uses constant per face corrected normal vector field to compute curvatures.
# "Al" vol file ./examples/geometry/meshes/digpoly-curvature-measures-cnc-3d torus 10 0.5 1.0 Const
outputs
Using face-*Constant* Corrected Normal Current - surface has 2584 surfels. [SurfaceMesh (OK) #V=2584 #VN=0 #E=5168 #F=2584 #FN=0 E[IF]=4 E[IV]=4 E[IFE]=2] - CTrivial normal t-ring=3 (discrete) Expected mean curvatures: min=0.125 max=0.3125 Computed mean curvatures: min=0.118944 max=0.365712 Expected Gaussian curvatures: min=-0.125 max=0.0625 Computed Gaussian curvatures: min=-0.214727 max=0.09246 |H-H_CNC|_oo = 0.0798986 |H-H_CNC|_2 = 0.0274956 |G-G_CNC|_oo = 0.0897268 |G-G_CNC|_2 = 0.0176866
This second example uses vertex-interpolated corrected normal vector field to compute curvatures.
./examples/geometry/meshes/digpoly-curvature-measures-cnc-3d torus 10 0.5 1.0 Interp
outputs
Using vertex-*Interpolated* Corrected Normal Current - surface has 2584 surfels. [SurfaceMesh (OK) #V=2584 #VN=0 #E=5168 #F=2584 #FN=0 E[IF]=4 E[IV]=4 E[IFE]=2] - CTrivial normal t-ring=3 (discrete) Expected mean curvatures: min=0.125 max=0.3125 Computed mean curvatures: min=0.146652 max=0.33483 Expected Gaussian curvatures: min=-0.125 max=0.0625 Computed Gaussian curvatures: min=-0.1556 max=0.0751507 |H-H_CNC|_oo = 0.0576324 |H-H_CNC|_2 = 0.0201468 |G-G_CNC|_oo = 0.0320427 |G-G_CNC|_2 = 0.00918083
It also produces several OBJ files to display curvature estimation results, example-cnc-H.obj and example-cnc-G.obj as well as the associated MTL file.
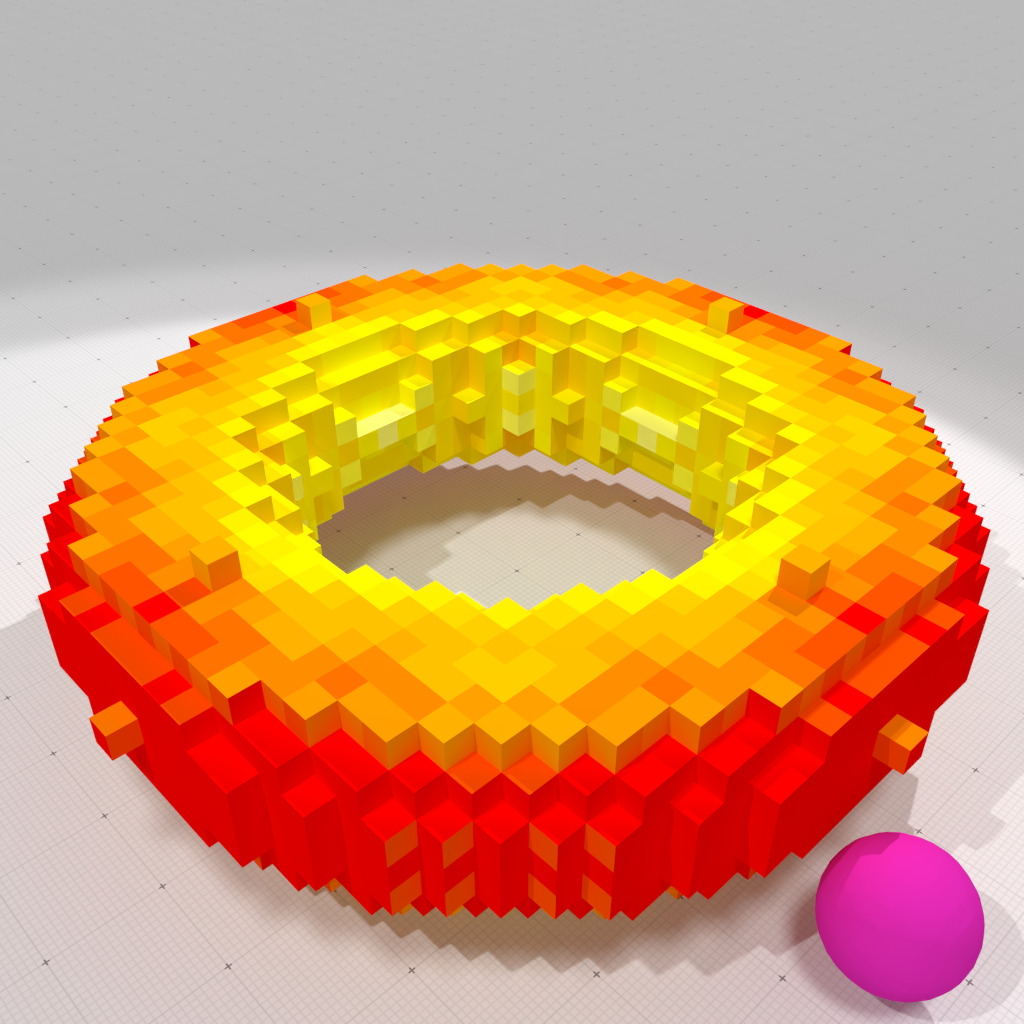
Face-constant corrected mean curvature measure, r=1 | 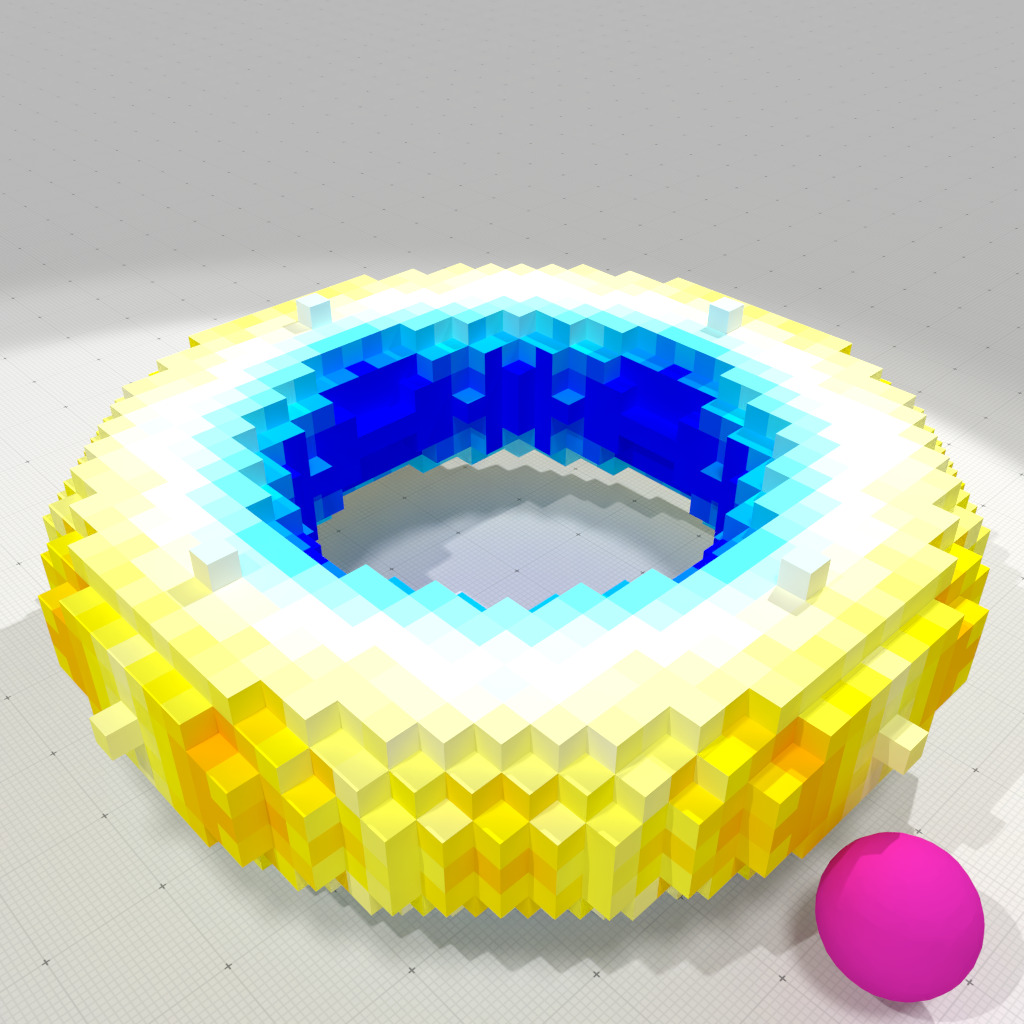
Face-constant corrected Gaussian curvature measure, r=1 | 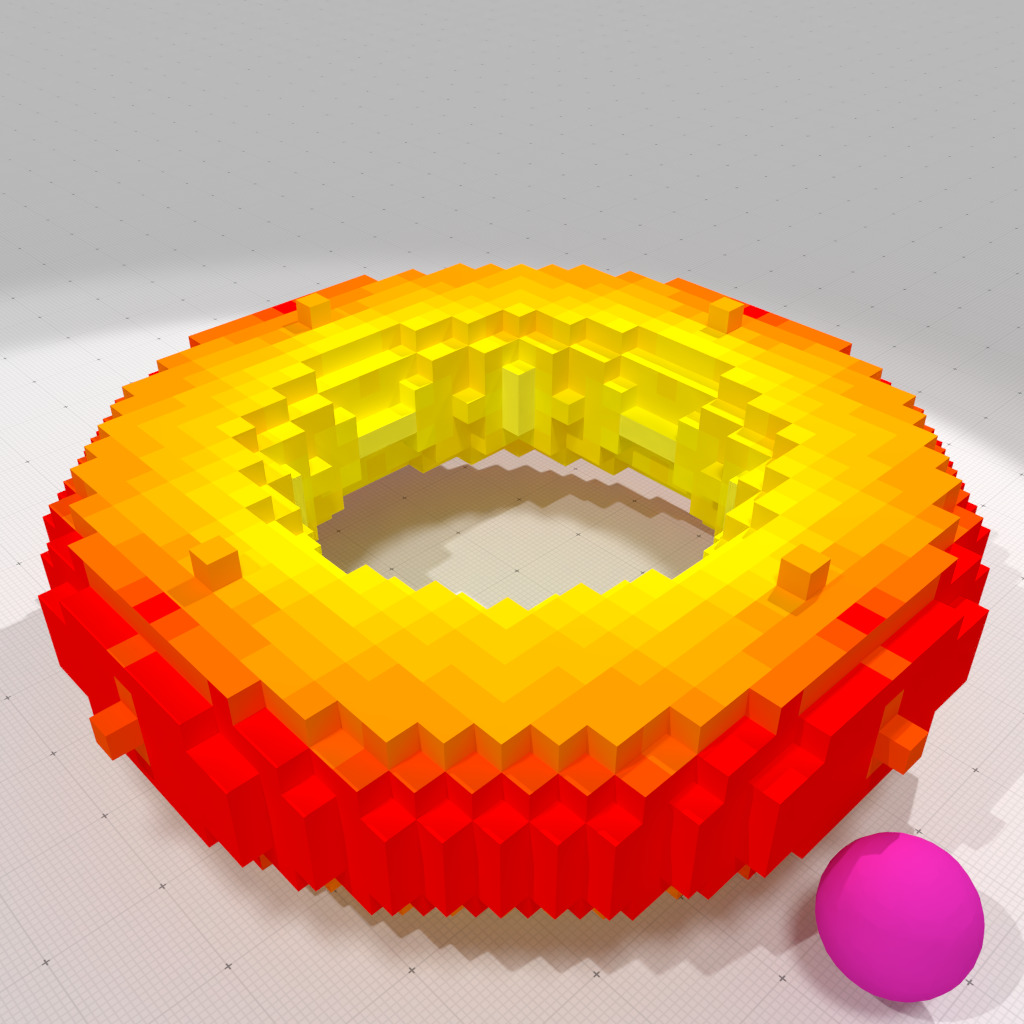
Vertex-interpolated corrected mean curvature measure, r=1 | 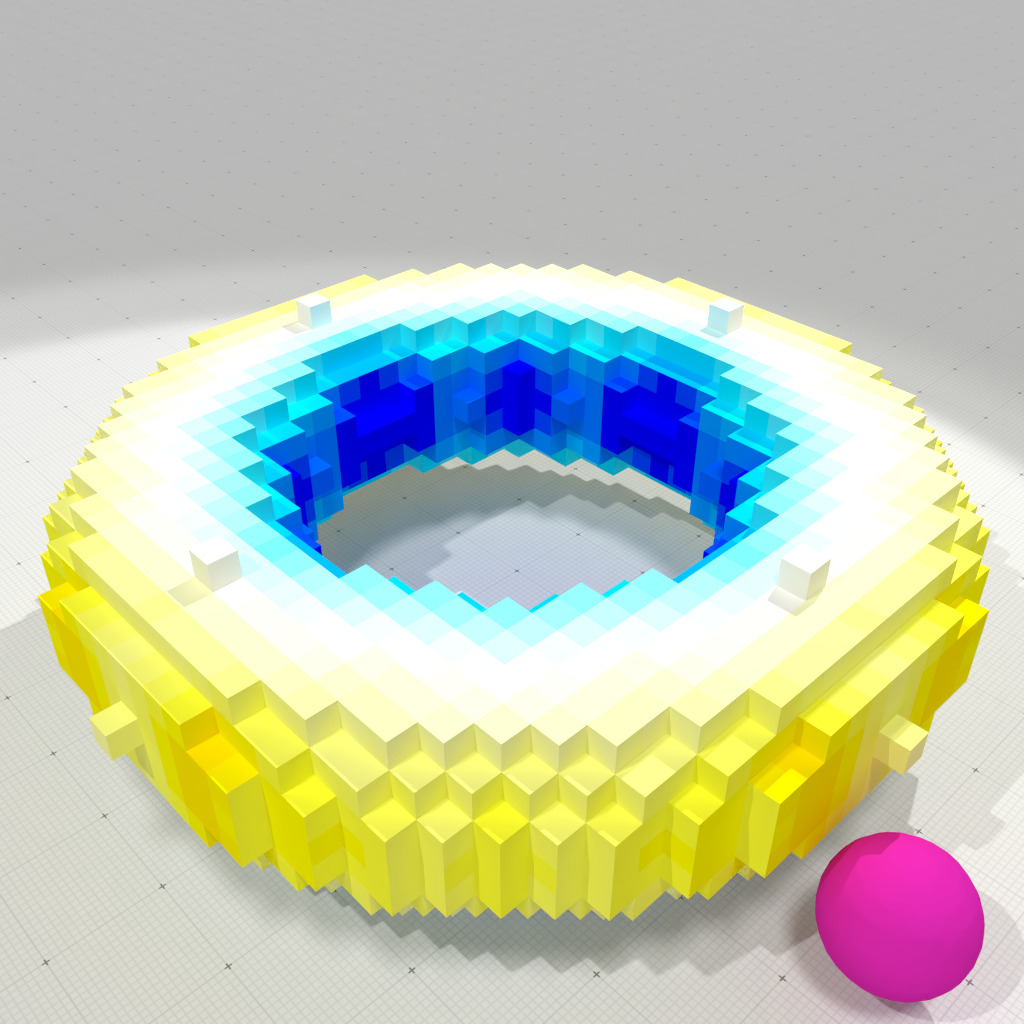
Vertex-interpolated corrected Gaussian curvature measure, r=1 |
- Note
- In opposition with Normal Cycle curvature measures, constant or interpolated corrected curvature measures can take into account an external normal vector field to estimate curvatures with better accuracy.
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include "DGtal/base/Common.h"
#include "DGtal/shapes/SurfaceMesh.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/meshes/CorrectedNormalCurrentComputer.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/Shortcuts.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/ShortcutsGeometry.h"
#include "DGtal/io/writers/SurfaceMeshWriter.h"
#include "DGtal/io/colormaps/GradientColorMap.h"
#include "DGtal/io/colormaps/QuantifiedColorMap.h"
{
DGtal::GradientColorMap< double > gradcmap( min_value, max_value );
gradcmap.addColor( DGtal::Color( 0, 255, 255 ) );
gradcmap.addColor( DGtal::Color( 255, 255, 255 ) );
gradcmap.addColor( DGtal::Color( 255, 255, 0 ) );
gradcmap.addColor( DGtal::Color( 255, 0, 0 ) );
return gradcmap;
}
{
using namespace DGtal;
using namespace DGtal::Z3i;
std::cout << "Usage: " << std::endl
<< "\t" << argv[ 0 ] << " <P> <B> <h> <R> <mode>" << std::endl
<< std::endl
<< "Computation of mean and Gaussian curvatures on an " << std::endl
<< "digitized implicit shape using constant or " << std::endl
<< "interpolated corrected curvature measures (based " << std::endl
<< "on the theory of corrected normal currents)." << std::endl
<< "- builds the surface mesh from polynomial <P>" << std::endl
<< "- <B> defines the digitization space size [-B,B]^3" << std::endl
<< "- <h> is the gridstep digitization" << std::endl
<< "- <R> is the radius of the measuring balls" << std::endl
<< "- <mode> is either Const for constant corrected normal" << std::endl
<< " vector field or Interp for interpolated corrected" << std::endl
<< " normal vector field." << std::endl
<< "It produces several OBJ files to display mean and" << std::endl
<< "Gaussian curvature estimation results: `example-cnc-H.obj`" << std::endl
<< "and `example-cnc-G.obj` as well as the associated MTL file." << std::endl;
std::cout << "You may either write your own polynomial as 3*x^2*y-z^2*x*y+1" << std::endl
<<"or use a predefined polynomial in the following list:" << std::endl;
auto L = SH::getPolynomialList();
for ( const auto& p : L )
}
{
if ( argc <= 1 )
{
usage( argv );
return 0;
}
using namespace DGtal;
using namespace DGtal::Z3i;
typedef Shortcuts< KSpace > SH;
std::string poly = argv[ 1 ]; // polynomial
const double h = argc > 3 ? atof( argv[ 3 ] ) : 1.0; // gridstep
const double R = argc > 4 ? atof( argv[ 4 ] ) : 2.0; // radius of measuring ball
std::string mode = argc > 5 ? argv[ 5 ] : "Const"; // either Const or Interp
bool interpolated = mode == "Interp";
if ( interpolated )
std::cout << "Using vertex-*Interpolated* Corrected Normal Current" << std::endl;
else
std::cout << "Using face-*Constant* Corrected Normal Current" << std::endl;
// Read polynomial and build digital surface
auto params = SH::defaultParameters() | SHG::defaultParameters();
params( "t-ring", 3 )( "surfaceTraversal", "Default" );
params( "polynomial", poly )( "gridstep", h );
params( "offset", 3.0 );
auto shape = SH::makeImplicitShape3D( params );
auto dshape = SH::makeDigitizedImplicitShape3D( shape, params );
auto bimage = SH::makeBinaryImage( dshape, params );
if ( bimage == nullptr )
{
<< poly.c_str() << ">" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
auto sembedder = SH::getSCellEmbedder( K );
auto embedder = SH::getCellEmbedder( K );
auto surfels = SH::getSurfelRange( surface, params );
SM smesh;
std::vector< SM::Vertices > faces;
SH::Cell2Index c2i;
auto pointels = SH::getPointelRange( c2i, surface );
auto vertices = SH::RealPoints( pointels.size() );
std::transform( pointels.cbegin(), pointels.cend(), vertices.begin(),
[&] (const SH::Cell& c) { return h * embedder( c ); } );
{
SM::Vertices face;
for ( auto&& primal_vtx : primal_surfel_vtcs )
face.push_back( c2i[ primal_vtx ] );
faces.push_back( face );
}
faces.cbegin(), faces.cend() );
auto exp_H = SHG::getMeanCurvatures( shape, K, surfels, params );
auto exp_G = SHG::getGaussianCurvatures( shape, K, surfels, params );
// Builds a CorrectedNormalCurrentComputer object onto the SurfaceMesh object
CNC cnc( smesh );
// Estimates normal vectors using Convolved Trivial Normal estimator
auto face_normals = SHG::getCTrivialNormalVectors( surface, surfels, params );
// Set corrected face normals => Corrected Normal Current with
// constant per face corrected vector field.
smesh.setFaceNormals( face_normals.cbegin(), face_normals.cend() ); // CCNC
// Set corrected vertex normals => Corrected Normal Current with
// smooth linearly interpolated per face corrected vector field.
if ( interpolated ) smesh.computeVertexNormalsFromFaceNormals(); // ICNC
// computes area, mean and Gaussian curvature measures
auto mu0 = cnc.computeMu0();
auto mu1 = cnc.computeMu1();
auto mu2 = cnc.computeMu2();
// estimates mean (H) and Gaussian (G) curvatures by measure normalization.
std::vector< double > H( smesh.nbFaces() );
std::vector< double > G( smesh.nbFaces() );
for ( size_t f = 0; f < smesh.nbFaces(); ++f )
{
const auto b = smesh.faceCentroid( f );
const auto area = mu0.measure( b, R, f );
H[ f ] = cnc.meanCurvature ( area, mu1.measure( b, R, f ) );
G[ f ] = cnc.GaussianCurvature( area, mu2.measure( b, R, f ) );
}
auto G_min_max = std::minmax_element( G.cbegin(), G.cend() );
auto exp_H_min_max = std::minmax_element( exp_H.cbegin(), exp_H.cend() );
auto exp_G_min_max = std::minmax_element( exp_G.cbegin(), exp_G.cend() );
std::cout << "Expected mean curvatures:"
<< " min=" << *exp_H_min_max.first << " max=" << *exp_H_min_max.second
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Computed mean curvatures:"
<< " min=" << *H_min_max.first << " max=" << *H_min_max.second
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Expected Gaussian curvatures:"
<< " min=" << *exp_G_min_max.first << " max=" << *exp_G_min_max.second
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Computed Gaussian curvatures:"
<< " min=" << *G_min_max.first << " max=" << *G_min_max.second
<< std::endl;
const auto error_H = SHG::getScalarsAbsoluteDifference( H, exp_H );
const auto stat_error_H = SHG::getStatistic( error_H );
const auto error_H_l2 = SHG::getScalarsNormL2( H, exp_H );
const auto error_G = SHG::getScalarsAbsoluteDifference( G, exp_G );
const auto stat_error_G = SHG::getStatistic( error_G );
const auto error_G_l2 = SHG::getScalarsNormL2( G, exp_G );
// Remove normals for better blocky display.
smesh.vertexNormals() = SH::RealVectors();
smesh.faceNormals() = SH::RealVectors();
const double Hmax = std::max( fabs( *exp_H_min_max.first ),
fabs( *exp_H_min_max.second ) );
const double Gmax = std::max( fabs( *exp_G_min_max.first ),
fabs( *exp_G_min_max.second ) );
auto colorsH = SMW::Colors( smesh.nbFaces() );
auto colorsG = SMW::Colors( smesh.nbFaces() );
for ( size_t i = 0; i < smesh.nbFaces(); i++ )
{
colorsH[ i ] = colormapH( H[ i ] );
colorsG[ i ] = colormapG( G[ i ] );
}
SMW::writeOBJ( "example-cnc-H", smesh, colorsH );
SMW::writeOBJ( "example-cnc-G", smesh, colorsG );
return 0;
}
Definition testPartialTemplateSpecialization.cpp:63
Aim: This class template may be used to (linearly) convert scalar values in a given range into a colo...
Definition GradientColorMap.h:120
void addColor(const Color &color)
Aim: This class is used to simplify shape and surface creation. With it, you can create new shapes an...
Definition ShortcutsGeometry.h:79
Aim: This class is used to simplify shape and surface creation. With it, you can create new shapes an...
Definition Shortcuts.h:102
std::ostream & error()
std::ostream & info()
DGtal::GradientColorMap< double > makeColorMap(double min_value, double max_value)
[curvature-comparator-Includes]
Definition curvature-comparator-ii-cnc-3d.cpp:89
Z3i this namespace gathers the standard of types for 3D imagery.
DGtal is the top-level namespace which contains all DGtal functions and types.
Definition ClosedIntegerHalfPlane.h:49
QuantifiedColorMap< TColorMap > makeQuantifiedColorMap(TColorMap colormap, int nb=50)
Definition QuantifiedColorMap.h:113
Trace trace
std::pair< typename graph_traits< DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > >::vertex_iterator, typename graph_traits< DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > >::vertex_iterator > vertices(const DGtal::DigitalSurface< TDigitalSurfaceContainer > &digSurf)
STL namespace.
Aim: Utility class to compute curvature measures induced by (1) a corrected normal current defined by...
Definition CorrectedNormalCurrentComputer.h:70
Aim: An helper class for writing mesh file formats (Waverfront OBJ at this point) and creating a Surf...
Definition SurfaceMeshWriter.h:65
Aim: Represents an embedded mesh as faces and a list of vertices. Vertices may be shared among faces ...
Definition SurfaceMesh.h:92