Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
topology/ctopo-1s-3d.cpp
A simple example of cellular grid space with several cells instantiated and visualized in 3D. This program outputs this image.
- See also
- Cells may be unsigned or signed
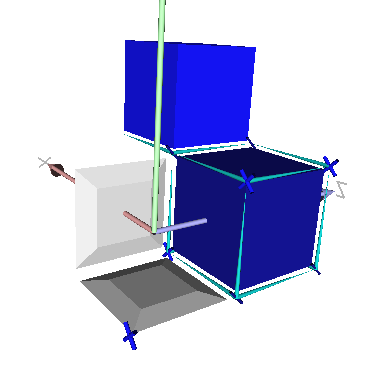
#include <iostream>
#include "DGtal/base/Common.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/StdDefs.h"
#include "DGtal/io/viewers/PolyscopeViewer.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DGtal;
using namespace DGtal::Z3i;
{
// for 3D display with PolyscopeViewer
Point plow(0,0,0);
Point pup(3,3,2);
K.init( plow, pup, true );
viewer << ptlow << ptup1 << ptup2;
// drawing cells of dimension 0
viewer << p1 << p2 << p3 << p4 << p5 << p6 << p7 << p8;
// drawing Cells of dimension 1
viewer << linel0<< linel1<< linel2 << linel3 ;
viewer << linel4<< linel5<< linel6 << linel7 ;
viewer << linel8<< linel9<< linel10 << linel11 << linel12;
// drawing cells of dimension 2
viewer << surfelA << surfelB << surfelC;
// drawing cells of dimension 3
viewer << vox1 << vox2;
viewer.show();
return 0;
}
Definition PolyscopeViewer.h:56
Definition testClone2.cpp:346
Z3i this namespace gathers the standard of types for 3D imagery.
DGtal is the top-level namespace which contains all DGtal functions and types.
Definition ClosedIntegerHalfPlane.h:49
STL namespace.